Today’s Traveller teams up with the Institute of Hotel Management, Aurangabad (IHM Aurangabad) in a dynamic and progressive initiative – #HospitalityFirst – that will bring incisive reports and data-based analysis to the current situation and solutions for the Hospitality industry for its long term health and sustainability.
In this article, Gautam Sen, Associate Professor – Operations Management at Institute of Hotel Management- Aurangabad (IHM Aurangabad) shares insights on the new industry dynamics and major challenges that restaurants face in taking technology adoption decisions.

Today’s Traveller: What are the challenges of emerging technology adoption in the restaurant business?
Gautam Sen – IHM Aurangabad: The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has necessitated a wider focus on technology use in restaurant operations. From online ordering to self-service, and touchless payment to remote delivery preference, the restaurant industry has had to adopt innovative digital solutions to manage customer experience.
A research by Edelman and Accenture suggests that, trust, responsiveness, and human interactions are key to create customer experiences in the post-pandemic world. The restaurant business is part of the people-oriented service industry where human interactions influence customer service experiences.
The application of emerging technologies like Self-service Technology (SST), Virtual Reality (VR), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Robots offers restaurants an opportunity to engage customers through innovative service experiences and increase operational efficiency. The two major challenges restaurants face in taking technology adoption decisions are:
- Identification of relevant technology to support unique business needs
- Implementation of technology to curate intended customer experience
Today’s Traveller: What are relevant approaches towards technology adoption by restaurants?
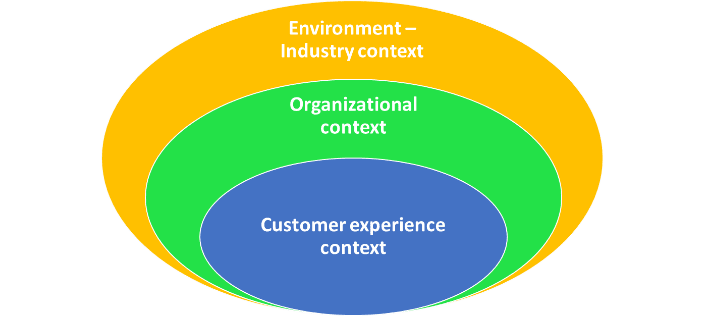
Gautam Sen – IHM Aurangabad: Technology adoption in restaurants depends on the customer’s perceived value of technology usage in the dining process. Customers’ perceived dining values towards different types of restaurants lead to a varying degree of expectations toward technology usage. The study suggests customers’ dining value focus is primarily utilitarian in quick-service restaurants, while predominately hedonic in fine-dining restaurants. (Jeong et al., 2020)
For the restaurant industry, technology adoption approaches have mainly centered on:
- Technology acceptance behaviour (at the customer level), where customers’ intentions to use technology have played a dominant explanatory role.
- Task-technology fit behaviour (at the organization level), where decisions are primarily based on tech-specific qualities.
Approaches that are made up of technical and situational traits downplay the importance of individual qualities in adopting technology and place a higher emphasis on usefulness. Both utilitarian (rational) and hedonic (emotional) dimensions are crucial in understanding the customers’ experience of technological innovations in restaurants.
Environmental characteristics (public readiness for technology, social aspirations, and conducive regulatory frameworks) and organizational characteristics (technological adaptability, resource availability, perceived operational benefits, and managerial implications) also impact a restaurant’s decision to adopt the technology. To determine the nested complexities of real-life technology adoption based on customers’ and restaurant operators’ preferences for interactive self-service technologies, a multilevel examination is required.
Today’s Traveller: How can restaurants apply a multilevel model approach for technology adoption?
Gautam Sen – IHM Aurangabad: Customer and restaurant preferences for innovative technologies are influenced by the business environment, organizational factors, technology attributes, service task characteristics, customer profiles, and customer experiences. The model assists restaurants with a three-step process to take effective technology adoption decisions, gain valuable insights into the technology & human interplay in service design and delivery, and determine inputs for future technology developments.
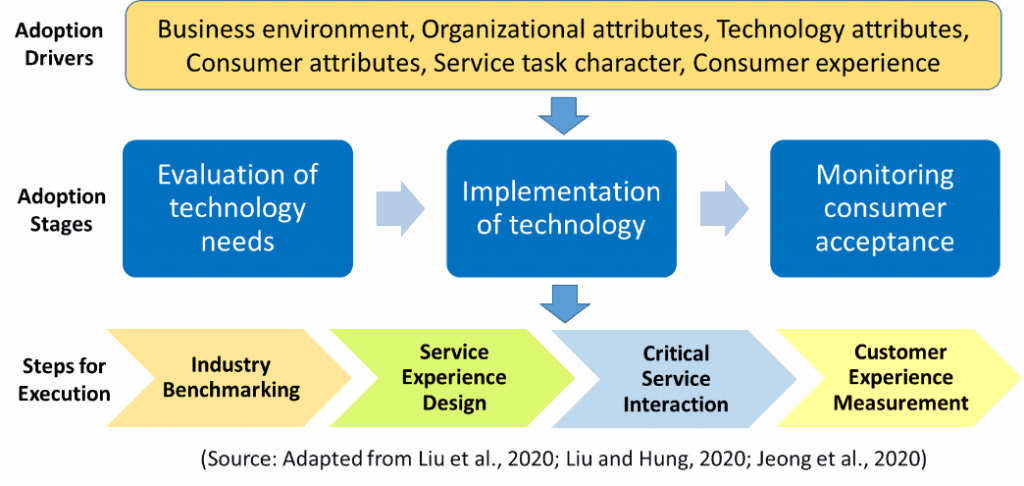
Evaluation of technology needs:
Restaurants should evaluate the influence of industry practices, technological developments, customer familiarity, resource availability, and regulatory frameworks on customers’ and restaurants’ technology preferences. The outcome will support technology benchmarking and the identification of relevant technology suitable for a restaurant.
Implementation of technology:
This is the most critical stage for technology incorporation emphasising on customization of adopted technology and service delivery. Customization and personalization of technology will be crucial for designing a technology-enabled service experience for customers.
Restaurants should assess their organizational goals, perceived benefits, managerial implications, and stakeholders’ preferences. The participation of technology developers in the process will be significant. Service interaction is the next step in the process where customers, service providers, and technology will co-produce service delivery moderated by the nature of the service task. Customer and service provider profiles with technology preferences will influence the outcome.
Monitoring consumer acceptance:
Restaurants must monitor customer experience based on critical service interactions that provide relevant insight on customer and business acceptance of technology for tech-enabled services. Customer experiences must be measured in a multi-dimensional structure (hedonic, utilitarian, and social experiences) to gauge the impact on technology preferences. This process will also provide valuable insights into the impact of various technology drivers on technology acceptance behaviour at multiple layers of the adoption model.
Today’s Traveller: What is the way forward?
Gautam Sen – IHM Aurangabad: Restaurants must carry out a logical and progressive examination of interactions between the external environment, organizational context, and critical service interactions between customers, technology, and the task on hand. This will help restaurants in achieving effective technology adoption.
Going forward, scrutiny of technology features, operational complexities, environmental factors, customer profiles, and task characteristics will provide restaurants with essential inputs for enhanced customer experience management through technology-driven services, and consistency in the application process.
Read More: Hospitality First



