In 2025, deep breathing is emerging as a powerful tool to combat professional burnout, where anxiety disrupts focus and efficiency. Science-backed techniques can help manage stress, enhance resilience, and boost productivity.

Anxiety is more prevalent than ever, affecting millions worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), around 301 million people struggle with an anxiety disorder. While therapy and medication remain key treatments, natural solutions like deep breathing are gaining recognition for their ability to ease stress and promote relaxation.
Deep breathing isn’t a new concept—it has been a core part of yoga, tai chi, and meditation for centuries. But does it really work? Science is catching up with ancient wisdom, confirming that deep breathing can help calm the mind and reduce anxiety. Let’s explore how it works and the practical ways you can use it to regain control in stressful situations.
The Science Behind Deep Breathing and Anxiety
Our body’s stress response is controlled by the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which is split into two parts: the Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS)—responsible for the ‘fight or flight’ reaction, increasing heart rate and adrenaline—and the Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS), which slows things down, promoting relaxation and restoring balance.
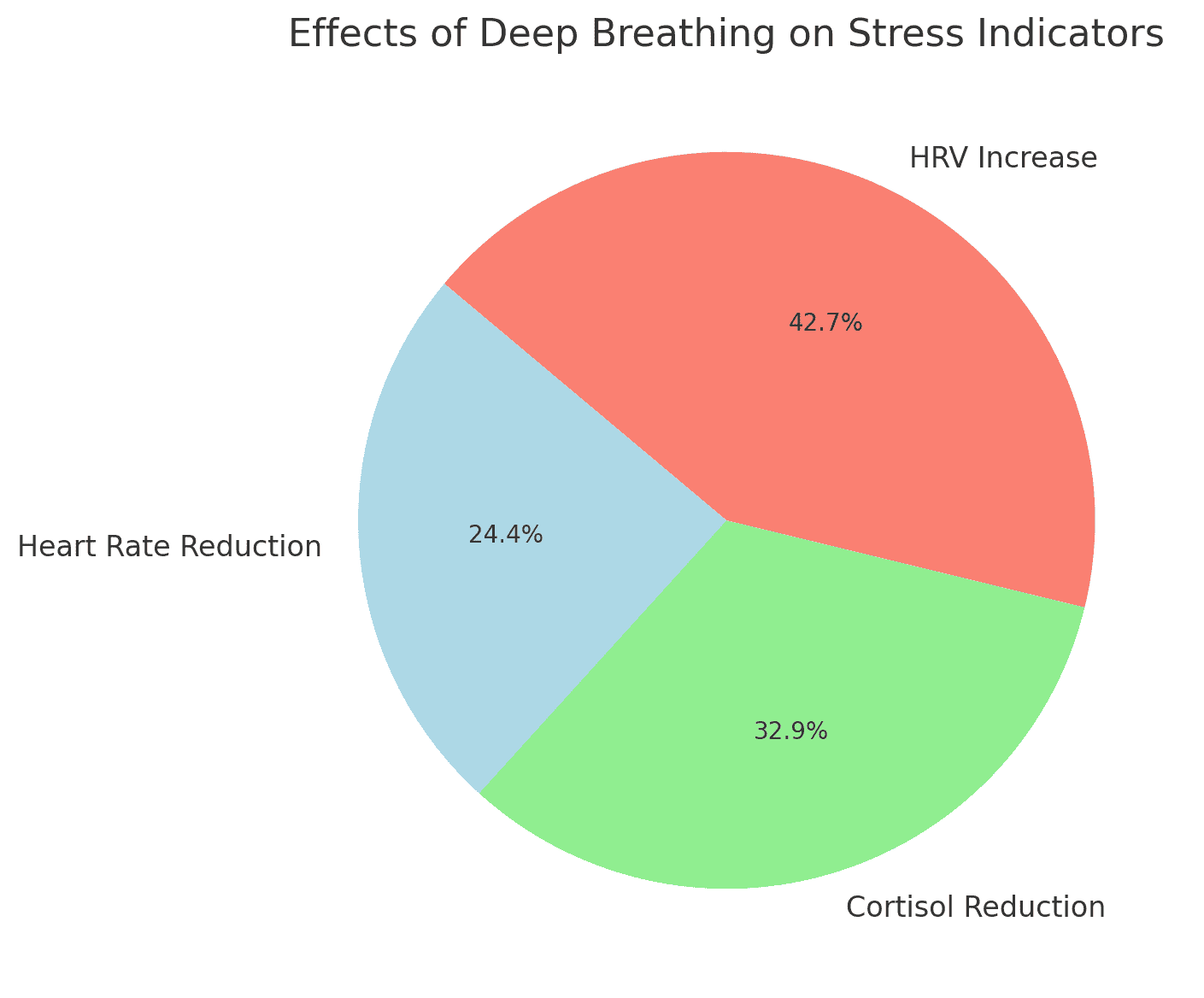
Deep breathing stimulates the vagus nerve, a crucial link to activating the PNS and encouraging a state of calm. Research supports this. Studies show that slow, controlled breathing reduces cortisol (the stress hormone) and increases heart rate variability (HRV), a sign of relaxation. Research from Harvard Medical School suggests that deep breathing helps the brain process emotions better by strengthening the connection between the amygdala (the fear centre) and the prefrontal cortex (the rational part of the brain). Another study found that combining deep breathing with progressive muscle relaxation significantly reduces muscle tension—one of anxiety’s most common physical symptoms.
Additionally, deep breathing improves oxygen circulation, ensuring the brain and muscles receive adequate nourishment. This can prevent common anxiety symptoms such as dizziness, brain fog, and fatigue. With consistent practice, deep breathing can rewire the brain to respond more calmly to stress, making it a long-term solution rather than just a temporary fix.
How Deep Breathing Helps Reduce Anxiety
When we’re anxious, we tend to breathe quickly and shallowly. This can throw off the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood, leading to dizziness, muscle tightness, and even more anxiety. Deep breathing works by restoring balance, engaging the relaxation response, and reducing the flood of adrenaline that fuels anxious thoughts and sensations. It also enhances mindfulness by shifting focus from racing thoughts to the rhythm of the breath.

Moreover, deep breathing influences the limbic system, the part of the brain that controls emotions. By slowing the breath, we send a signal to the brain that we are safe, reducing the likelihood of a full-blown panic response. This physiological shift can be particularly beneficial for individuals with generalised anxiety disorder (GAD) and panic disorder.
Deep Breathing Techniques That Work
Not all breathing exercises are the same—here are some of the most effective techniques for reducing anxiety:
Diaphragmatic (Belly) Breathing
Sitting or lying down, place one hand on your chest and the other on your stomach. Inhale deeply through your nose, making sure your stomach expands while your chest stays still. Exhale slowly through your mouth. Practising this for a few minutes daily can help regulate stress responses and create a sense of calm. Over time, this technique can improve lung capacity and enhance overall breathing efficiency.
Box Breathing
This technique, popular among Navy SEALs for staying calm under pressure, involves inhaling for four seconds, holding for four seconds, exhaling for four seconds, and holding again for four seconds. This controlled breathing pattern helps slow the heart rate and clear the mind. Box breathing is especially useful in high-pressure situations, such as public speaking, interviews, or sudden moments of anxiety.
4-7-8 Breathing

Developed by Dr Andrew Weil, this method is particularly useful for bedtime anxiety. Inhale through your nose for four seconds, hold your breath for seven seconds, and exhale slowly through your mouth for eight seconds. Repeating this cycle a few times can help lower stress and improve sleep. This technique is ideal for those who experience nighttime restlessness or racing thoughts.
Alternate Nostril Breathing (Nadi Shodhana)
A practice rooted in yoga, this technique helps balance both hemispheres of the brain. Close your right nostril with your thumb and inhale through the left. Switch sides, exhaling through the right and inhaling again before alternating. Just a few minutes of this can create a deep sense of balance and relaxation. Studies suggest that this practice can also improve focus and mental clarity, making it beneficial for students and professionals alike.
Resonance Breathing
A simple technique for synchronising breath with the body’s natural rhythm, resonance breathing involves inhaling for five to six seconds and exhaling for the same amount of time. This steady, balanced breathing pattern helps regulate heart rate and improve overall well-being. Research has shown that resonance breathing can be particularly helpful in reducing symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and chronic stress.
Making Deep Breathing Part of Everyday Life
Deep breathing doesn’t need to be a time-consuming ritual—it can be effortlessly woven into your daily routine. A few minutes of diaphragmatic breathing in the morning sets a calm tone for the day. Before a stressful event like a presentation or an exam, box breathing can help keep nerves under control. The 4-7-8 method is a great tool for winding down before bed, easing anxiety-induced restlessness. In the middle of an anxiety attack, alternate nostril breathing can be an immediate grounding technique.
Beyond these planned moments, integrating deep breathing into spontaneous parts of the day, like during a commute, before responding to an email, or while waiting in a queue, can reinforce a habit of mindfulness. Over time, these small efforts can create significant changes in emotional regulation and resilience against stress.
What the Experts Say
The effectiveness of deep breathing isn’t just anecdotal,it’s backed by science. A meta-analysis of 16 studies found that deep breathing significantly reduces cortisol levels and increases HRV, both key markers of stress reduction. Dr Emma Seppälä, author of The Happiness Track, describes controlled breathing as an ‘off switch’ for stress. Meanwhile, neuroscientist Dr Andrew Huberman highlights the power of physiological sighing—two short inhales followed by a long exhale—as one of the quickest ways to calm the nervous system.

Breathing expert Patrick McKeown, author of The Oxygen Advantage, emphasises that many people are unknowingly breathing inefficiently, contributing to increased anxiety levels. By learning to breathe correctly and efficiently, individuals can improve their overall health and stress resilience.
Can Deep Breathing Really Reduce Anxiety?
The science is clear, deep breathing is a powerful, accessible tool for managing anxiety. While it may not replace therapy or medication in severe cases, it’s an excellent complementary practice for those looking to cultivate a greater sense of calm and control.
Incorporating breathing exercises into daily life allows you to take charge of your stress response, improve emotional regulation, and enhance overall well-being. Whether you need a moment of calm in the middle of a hectic day or a way to ease long-term anxiety, deep breathing is a free, simple, and scientifically backed solution that’s always within reach. By making small, consistent efforts to breathe better, you can gradually transform your relationship with stress and anxiety, leading to a healthier, more balanced life.
Read more – Latest



